CausalGPS | Example 1
Contents
CausalGPS | Example 1¶
Matching with parametric GPS model¶
In this example, we will use the CausalGPS R package to generate pseudo population based on parametric GPS model. We use synthetic Medicare data that is available in the package. All processing are done in R.
Step 1: Install and load the package
install.packages("CausalGPS")
library(CausalGPS)
Step 2: Load the data
data("synthetic_us_2010", package = "CausalGPS")
synthetic_us_2010$cdc_mean_bmi[synthetic_us_2010$cdc_mean_bmi > 9000] <- NA
data <- synthetic_us_2010
confounders_s1 <- c("cs_poverty","cs_hispanic",
"cs_black",
"cs_ed_below_highschool",
"cs_median_house_value",
"cs_population_density",
"cdc_mean_bmi","cdc_pct_nvsmoker",
"gmet_mean_summer_tmmx",
"gmet_mean_summer_rmx",
"gmet_mean_summer_sph",
"cms_female_pct", "region"
)
data$region <- as.factor(data$region)
Step 3: Generate Pseudo Population
set.seed(574)
ps_pop_obj_1 <- generate_pseudo_pop(data$cms_mortality_pct,
data$qd_mean_pm25,
data.frame(data[, confounders_s1, drop=FALSE]),
ci_appr = "matching",
gps_model = "parametric",
bin_seq = NULL,
trim_quantiles = c(0.25 ,
0.99),
optimized_compile = TRUE,
use_cov_transform = TRUE,
sl_lib = c("m_xgboost"),
params = list(xgb_nrounds=seq(10,60),
xgb_eta=seq(0.04, 0.4, 0.02)),
nthread = 12,
covar_bl_method = "absolute",
covar_bl_trs = 0.1,
covar_bl_trs_type= "maximal",
max_attempt = 10,
matching_fun = "matching_l1",
delta_n = 0.1,
scale = 1)
In the previous code, we trimmed data using trim_quantiles. This helps to focus on common support range. m_ in m_xgboost stands for modified xgboost library. So we can pass a range of hyperparameter with xgb_ prefix. Covariate balance has 3 options including method (which only absolute has been implemented so far), threshold (covar_bl_trs) and threshold type (covar_bl_trs_type) which includes mean, median, and maximal. max_attempt is the maximum number of attempts to generate pseudo population. matching_fun is the matching function (only matching_l1 has been implemented so far). delta_n is the size of caliper and scale is a specified scale parameter to control the relative weight that
is attributed to the distance measures of the exposure versus the GPS.
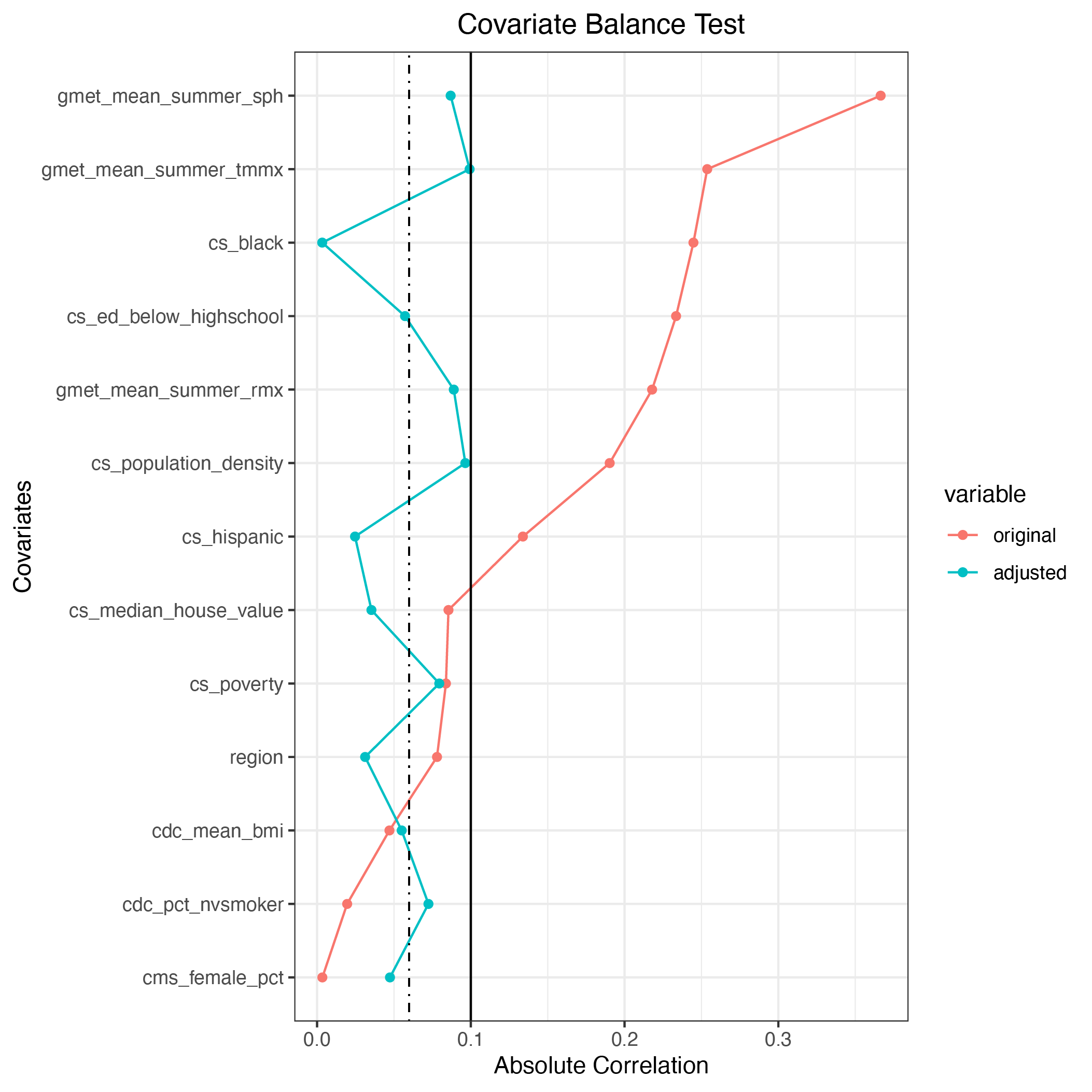
After 6 iterations, a covariate balance is achieved one can run summary to see the summary of the results.
summary(ps_pop_obj_1)
--- CausalGPS pseudo population object summary ---
Pseudo population met the covariate balance requirement: TRUE
Absolute correlation of the original data:
mean: 0.151
median: 0.134
maximal: 0.367
cs_poverty : 0.084
cs_hispanic : 0.134
cs_black : 0.245
cs_ed_below_highschool : 0.234
cs_median_house_value : 0.085
cs_population_density : 0.190
cdc_mean_bmi : 0.047
cdc_pct_nvsmoker : 0.020
gmet_mean_summer_tmmx : 0.254
gmet_mean_summer_rmx : 0.218
gmet_mean_summer_sph : 0.367
cms_female_pct : 0.003
region : 0.078
Absolute correlation of the pseudo population:
mean: 0.060
median: 0.057
maximal: 0.099
cs_poverty : 0.079
cs_hispanic : 0.025
cs_median_house_value : 0.003
cdc_mean_bmi : 0.057
cdc_pct_nvsmoker : 0.035
gmet_mean_summer_tmmx : 0.096
gmet_mean_summer_sph : 0.055
cms_female_pct : 0.072
cs_black : 0.099
cs_ed_below_highschool : 0.089
cs_population_density : 0.087
gmet_mean_summer_rmx : 0.047
region : 0.031
Hyperparameters used for the select population:
xgb_nrounds : 21
xgb_max_depth : 6
xgb_eta : 0.32
xgb_min_child_weight : 1
xgb_verbose : 0
Number of data samples: 2299
Number of iterations: 6
--- *** ---
It is important to note that the package ignores any data with missing values. As a result, number of data samples are different from the original data. We can also plot the covariate balance.
Now, we can conduct the analysis using the pseudo population.
set.seed(168)
erf <- estimate_npmetric_erf(m_Y = ps_pop_obj_1$pseudo_pop$Y,
m_w = ps_pop_obj_1$pseudo_pop$w,
counter_weight = ps_pop_obj_1$pseudo_pop$counter_weight,
bw_seq = seq(0.2,10,0.05),
w_vals = seq(7,13, 0.05),
nthread = 12)