Data Node
Each project in the system has a unique main data node (MainDataNode) that serves as the entry point for the project’s data. Whenever an instruction is applied to the main data node, a new data node (DataNode) object is created. By applying instructions on existing data nodes, new data nodes can be generated.
The newly generated data node is considered a “lazy” node, meaning it is not evaluated until it is needed. To force the evaluation of a data node, users can use the .compute() method. However, since no instructions are applied to the main data node, it does not have a .compute() method.
The parent node’s output data is the descendant node’s input data. Lazy nodes do not have any output data; as a result, users need to compute them before applying instructions to them.
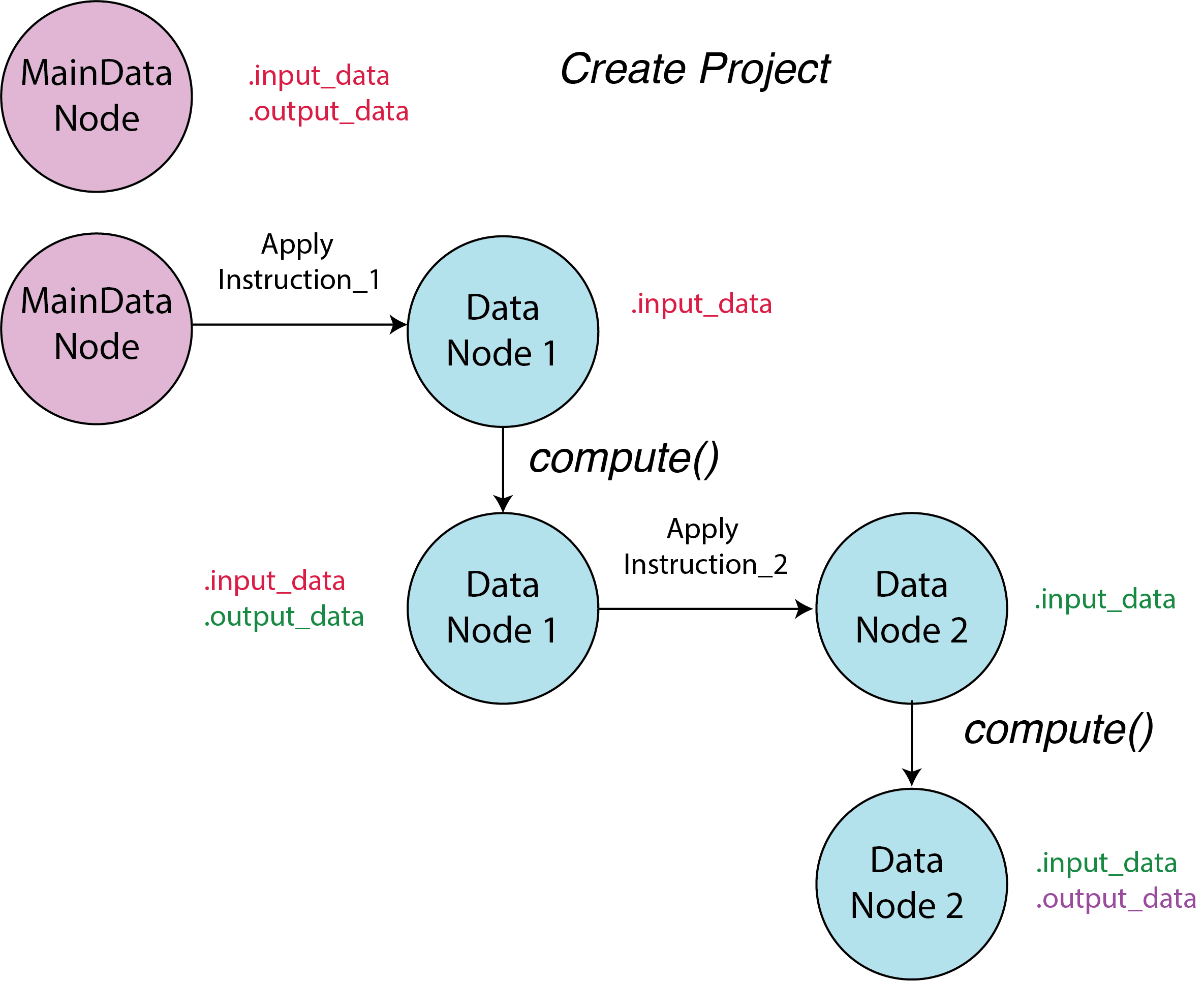
User can have access to data inside the node by .access_input_data() and .access_output_data() methods. The former returns the input data of the node, while the latter returns the output data of the node.
At a data node, one can see the history of instrucions from the root node (MainDataNode) to the current node by using .history() command. The decendents of the current node can be accessed by .decendents() method.